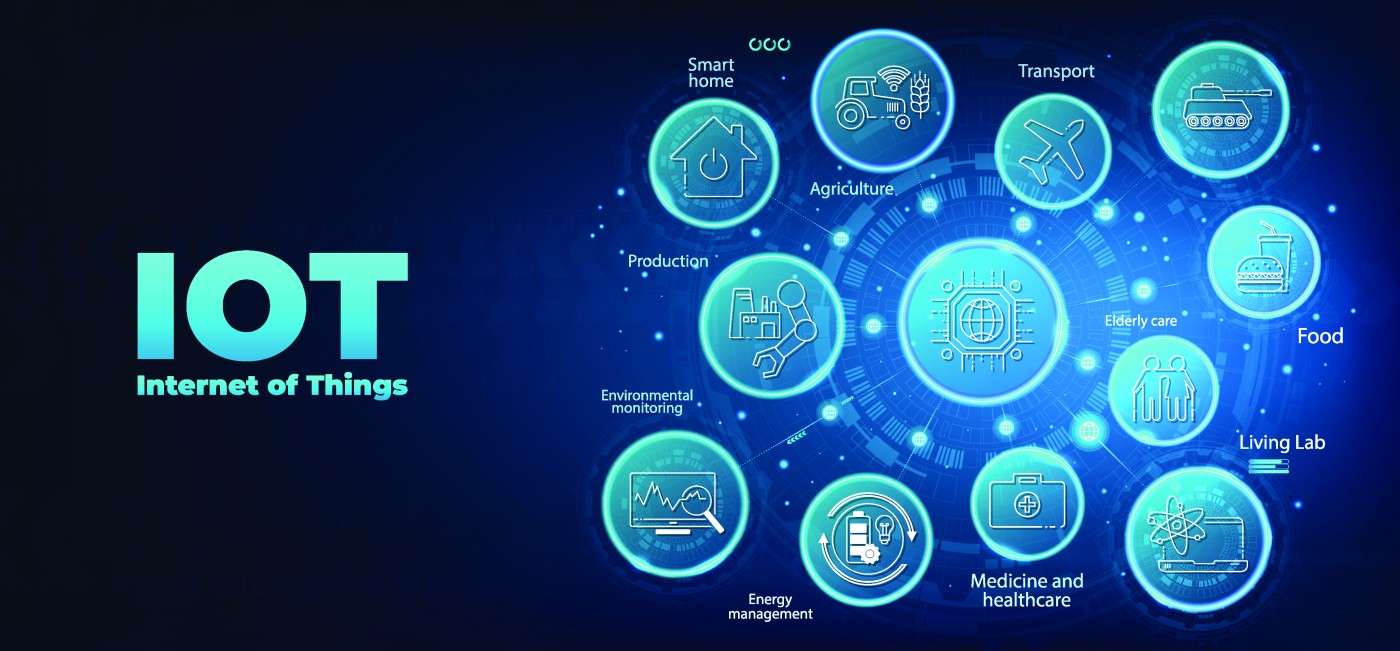
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of devices that allows them to communicate and exchange data with other smart devices over the Internet. The embedded sensors and software make these material things “smart.” In this post, we’ll explore the various applications of IoT and what its future looks like.
Contents
What is IoT (the Internet of Things)?
IoT enables seamless communication between people and things by connecting everyday utilities such as home appliances, security systems, kitchen appliances, thermostats, cars, baby monitors, and more via embedded unique identifiers (UIDs). The connected devices transmit data over the internet without needing human-to-computer interaction.
The number of connected mobile IoT devices is set to grow immensely and is expected to reach 3.5 billion by 2023. Organizations across the spectrum are using IoT to operate more effectively. IoT allows enterprises to improve decision-making, enhance customer service, and increase business value. Additionally, cloud platform availability empowers individuals and businesses to access and scale up infrastructure without managing it.
Here are some of the top applications of IoT
The IoT finds application in various private and public aspects of life.
Agriculture: The ever-increasing world population drives up the demand for agricultural products. However, the migration of young people to big cities destabilizes the human resource required for agricultural development. IoT and related technologies can be pivotal in automating farming processes and fulfilling food demand.
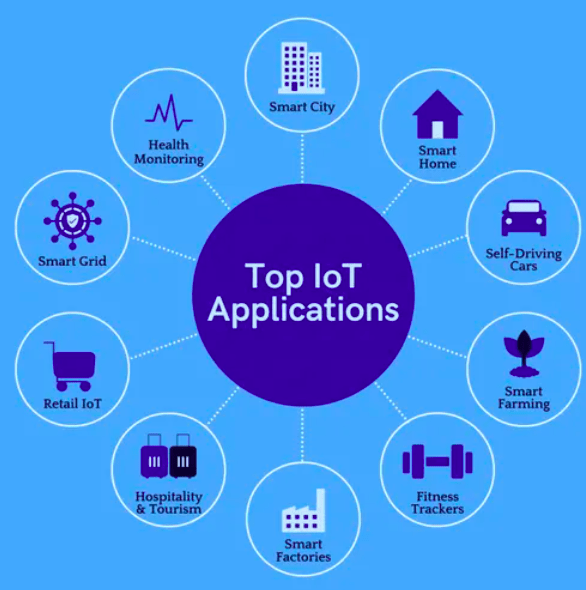
Consumer Applications: The Internet of Things makes people’s lives easier by monitoring and managing their lifestyles. There is a massive market for intelligent electronics, watches, television systems, health tracking, and virtual reality. In addition, IoT is leading the market with applications such as home security and personal asset tracking.
Healthcare: Wearable IoT devices provide a range of benefits to patients and healthcare providers alike. By extension, IoT enables healthcare professionals to monitor patients remotely. The devices can automatically collect patients’ health vitals like blood pressure, heart rate, temperature, and more.
Insurance: IoT is altering traditional business models like insurance. It simplifies and accelerates the claim and underwriting process. Besides reducing costs, digital networking via IoT generates additional revenues. Cross-selling and more significant customer interaction become a strategic component for insurers.
Manufacturing: The Internet of Things creates a more technically-driven environment for manufacturing industries. It can automatically track development cycles, facilitate the production flow, and manage inventories.
Retail: IoT devices can collect vital data on a product’s shopping lifecycle. Once this data is processed and analyzed, retail managers can make valuable decisions to improve retail operations and the customer experience.
Transportation: IoT applications integrate personal and commercial vehicles by improving communication and information distribution. Besides connecting consumers and goods, it offers benefits such as route optimization, automobile tracking, weather monitoring, distance coverage, and more.
Utilities/Energy: A grid can have IoT capabilities with intelligent meters, receivers, sensors, and energy boxes communicating. IoT applications in utilities generate revenue, improve efficiency, and conserve resources. Utility providers can keep up with the rising demand by optimizing energy and distribution with the help of IoT.
Traffic Monitoring: Intelligent traffic monitoring helps improve decision-making and achieve urban growth. An IoT-based system collects, processes, and analyzes real-time traffic data to provide updates on traffic incidents and congestion. In addition, early warning messages save commute time during peak hours.
Hospitality: Many hotels allow guests to control air conditioning, heating, or ventilation from a central location. Television control and greeting devices are also common. Moreover, Internet of Things devices alert the staff about various appliances’ operating status. As a result, technicians can fix critical appliances even before any major functionality loss occurs.

Water Supply: Water scarcity is a reality. IoT applications have a potential solution to monitor, control, and regulate the quality and usage of water. Besides, it also maintains associated equipment such as pumps, pipes, etc. Smart water technology connects water systems with people.
Fleet Management: IoT enables predictive fleet maintenance by boosting visibility, efficiency, and manageability. It helps to monitor cargo better and improves driver operation. In addition, IoT devices can predict maintenance and help replace parts before the issue gets too expensive.
Smart Pollution Control: IoT devices and attached sensors are stationed at key city locations. They monitor pollution levels and periodically upload data to the IoT cloud. The system then processes the information to trigger public actions such as diversions or road closures.
Smart Cities: A smart city has better public utilities, infrastructure, services, and more. Smart meters allow utility companies to regulate energy flow efficiently, while connected vehicles make public transit tremendously efficient. In addition, smart grids are coming up to conserve resources and lower peak hour stress.
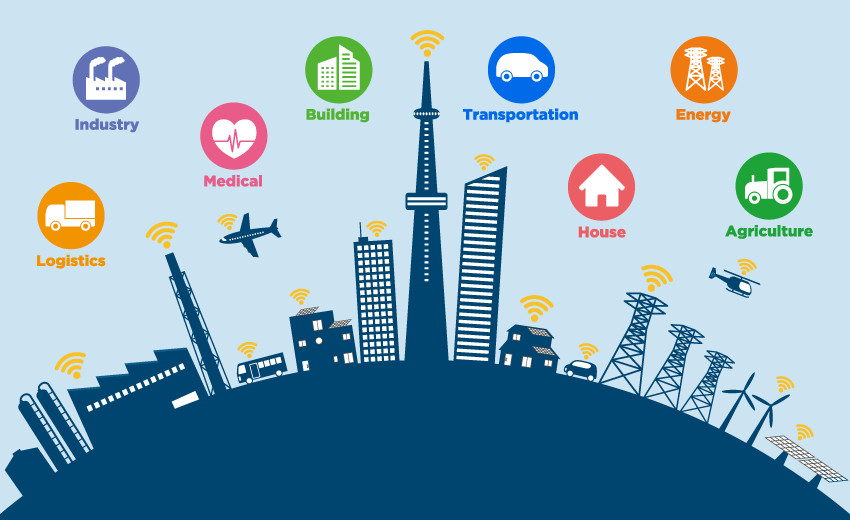
What is the way forward for IoT?
Fast-forward to 2025, and there’ll be more than 21 billion IoT devices. The connected technology can pave the way to increase energy efficiency, minimize waste, and nurture personal autonomy. First, however, the IoT architecture needs a rich feedback mechanism and a responsive system to make it sustainable.
IoT and AI can team up to drive intelligent actions from collected data. Together, they can predict, prescribe, and deliver an adaptive response. For example, they can detect fraudulent ATM behavior, increase equipment uptime by predicting maintenance, predict driver insurance premiums based on performance, and improve overall maintenance cost.
However, any budding technology is vulnerable, and applications of IoT are no different. Malicious malware is always on the prowl to access and affect connected devices. Such attacks can disrupt services and halt critical processes for hours. Therefore, security initiatives must be sharp enough to stop distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks.
FAQs:
1. What is the importance of IoT?
The Internet of Things, or IoT, is a rapidly evolving technological field that transforms any electronic device into a smarter one. Many industries are beginning to incorporate this technology into their operations in order to increase productivity and efficiency.
IoT applications aid in decision making, tracking and monitoring systems in real-time, and automating daily tasks for convenience.
This cutting-edge technology offers the user several features, including cloud data storage, a platform for analyzing the collected data, real-time analytics, etc., in addition to connecting the device to the internet. This technology can be integrated into almost any industry due to its broad range of applications.
2. Where is IoT mainly used?
IoT applications are primarily used to build smart homes and smart cities. IoT solutions are already in use in the following industries:
• Building and Home Automation
IoT can automate lighting, cooling, security systems, and other building functions.
• Automation and Optimization of Industrial Production
IoT systems reduce the need for manual labor while increasing the efficiency of industrial production processes.
• Public Utilities Administration
IoT systems can connect entire cities to reduce waste and improve access to public utilities.
• Information Technology
With network data collected by embedded IoT devices, digital communication hardware and software can be managed and optimized. Transportation and traffic management
3. What are the features of IoT?
The following are major IoT features:
- Connectivity: Establishing a proper connection between all IoT devices and the IoT platform, which could be a server or the cloud.
- Analyzing: After connecting all of the relevant things, it is time to analyze the data collected in real-time and use it to build effective business intelligence.
- Integrating: IoT integrates various models to improve user experience.
- Artificial Intelligence: IoT makes things smart and improves people’s lives by utilizing data.
- Sensing in IoT: In IoT technologies, sensor devices detect and measure environmental changes and report their status.
- Active Engagement: IoT allows connected technology, products, or services to engage in active engagement with one another.
- Endpoint Management: Endpoint management is critical for all IoT systems; otherwise, the system will fail completely.
4. What are examples of IoT devices?
Smartphones, watches, refrigerators, intelligent home security systems, fitness trackers, medical sensors, smart cooking appliances, and other IoT devices are examples.
- Sentri – Home Automation and Monitoring
Sentri is a one-stop technology hub for monitoring (babies, pets, and so on), controlling (lighting, locks, and so on), and personalizing (temperature, pictures, and so on) your home.
- Jawbone Up is a fitness tracker
Jawbone Up is a complete fitness tracking system in the form of a wristband. It has an infinite number of connections with third-party apps and also offers community-based data sharing.
- Smart Body Analyzer by Withings
This device is easily mistaken for a standard digital weighing scale, but it does much more. The system is based on four weight sensors and a body-positioning detector.
- Finger Reader – Fluid
This noble product is a wearable interface for visually impaired people to read on the go.
5. What are the four pillars of IoT?
The four pillars of IoT application are as follows:
1. Connecting people in more meaningful and valuable ways
The Internet has become an indispensable part of most people’s lives, and this is unlikely to change anytime soon.
2. Transforming data into intelligence in order to make better decisions
Sensors generate massive amounts of raw data for the purpose of analysis, but there is no standard format for storing and reusing it.
3. Providing the appropriate information to the appropriate person
If we want to learn something new and benefit from it, we must deliver it to the right person.
4. Using the right machine at the right time
The use of smart devices in our daily lives is also becoming more common.
6. What are the challenges of IoT?
The following are the various types of challenges that IoT faces:
IoT security challenges:
- Inadequate encryption
- Inadequate testing and updating
- Brute forcing and the dangers of using default passwords
- Ransomware and IoT Malware
- A cryptocurrency-focused IoT botnet.
Design challenge in IoT:
- Battery life is a limitation in IoT design
- Cost and time to market increases
- The system’s security.
IoT deployment challenges:
- Connectivity
- Platform independence
- Data collection and analysis
- Inadequate skill set.
7. What is IoT architecture?
IoT has four layers, which are as follows:
Sensing Layer – This layer contains sensors, devices, and actuators. They receive and process data (physical/environmental parameters) and then transmit it over a network.
Network Layer – This layer contains Internet/Network gateways and Data Acquisition Systems (DAS). Advanced gateways, which primarily connect sensor networks to the Internet, also perform many basic gateway functions such as malware protection, filtering, and decision making.
Data Processing Layer – This is the IoT ecosystem’s processing unit, where data is analyzed and pre-processed before being sent to the data center. Edge IT, or edge analytics, enters the picture here.
Application Layer – Data centers or the cloud are data management stages where the end-user applications, such as health care, agriculture, farming, aerospace, etc., manage and use data.