Contents
- 1 What is IoT (Internet of Things)?
- 2 How does IoT work?
- 3 History of IoT
- 4 What is the purpose of IoT in this 21st Century and why is it important?
- 5 What are the pros and cons of IoT?
- 6 Cons
- 7 What are the benefits of industrial IoT?
- 8 What are the IoT applications?
- 9 IoT standards and frameworks
- 10 IoT framework
- 11 FAQs
What is IoT (Internet of Things)?
IoT is a network of physical objects (‘things’) embedded with software, sensors, and other technologies connected to each other over the Internet. The underlying technology enables communication amidst the connected devices and the cloud as well as in-between the devices. True to its name, IoT helps connect everyday ‘things’ such as cars, vacuums, toothbrushes, and machines with the Internet. These devices leverage sensors to collect data and provide intelligent responses to the users. Such devices range from everyday household objects to complicated industrial tools.
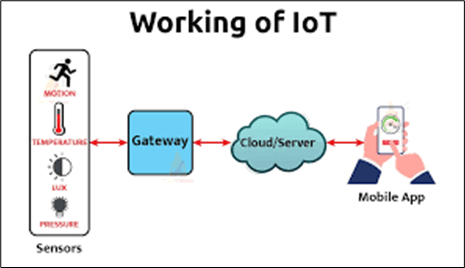
How does IoT work?
An IoT system collects and exchanges data in real time. It has three components:
- Smart device: Any device like a security camera or television that collects data from its environment and transfers data to and from the IoT application using the Internet.
- IoT application: It is a group of software and services engaged in the integration of data received from different IoT devices. The data is analysed using artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning (ML) technology to make intelligent decisions that are communicated back to the smart device. This is how the device can respond intelligently to the inputs received.
- Graphical user interface: The interface is utilized for managing an IoT device or a group of devices. For example, a website or a mobile application to control a smart device.
History of IoT
In the early 1980s, a few students from Carnegie Mellon University installed micro-switches to track the number of coke cans available in the Coca-Cola vending machine at the university. Further in 1990, a toaster was connected to the Internet by John Romkey. A year later, some students at Cambridge University programmed a web camera to take photographs of the coffee pots present in their computer lab. This helped in monitoring the quantity of coffee available in the pots.
Later in 1999, a computer scientist named Kevin Ashton coined the term, ‘Internet of things.’ During his time at Procter & Gamble (P&G), Ashton pioneered the use of radio frequency ID (RFID) technology on products for tracking as part of supply chain management. However, it was as early as 1832 that the idea of connected devices emerged—when the first electromagnetic telegraph was invented. The telegraph enabled direct communication between machines by transferring electrical signals.
What is the purpose of IoT in this 21st Century and why is it important?
In the 21st century, the IoT has seamlessly accelerated communication between people, devices, and processes. Almost everyone we know has one or more connected devices at home. Everyday objects such as light bulbs, thermostats, cars, and kitchen appliances are connected to the Internet. Undoubtedly, the IoT has helped integrate human communications in ways we could hardly imagine.
Diverse industries such as oil and gas, mining, automotives, utilities, and manufacturing utilise IoT for supply chain management, data collection, and driving predictive analytics and AI. The presence of a network of embedded devices connected to vehicles, equipment, and appliances across warehouses and manufacturing floors helps organisations take advantage of real-time process monitoring. In this way, organisations are also better equipped for faster decision-making.
A few noteworthy advantages of the IoT are:
- Low-power, low-cost sensor technology
- Enhanced connectivity
- Ability to access infrastructure easily in the case of businesses
- Advancement in ML and Analytics
- Conversational AI.
What are the pros and cons of IoT?
Like the two sides of a coin, the IoT too has its pros and cons. Let us examine them in detail:
Pros
- Minimal human efforts: Communication between IoT devices enables automation of tasks to enhance quality of service and minimise human intervention.
- Timesaving: Reduction of human efforts ultimately helps save time, which can be used to focus on other high-priority activities.
- Real-time information access: Irrespective of our physical locations, IoT devices enable anytime, anywhere access to useful information in real-time.
- Security benefits: IoT devices operating as part of an interconnected system facilitate smarter control of homes through mobile phones. This improves security and provides protection at an individual level as well.
Cons
- Heavy dependency on the Internet: IoT devices can not function in the absence of the Internet. Therefore, they are of no use in areas subject to low or poor Internet connectivity.
- Lack of global standards: There are no globally accepted standards of compatibility for IoT devices. Therefore, two devices manufactured by two different companies operating as part of a single network might not be able to communicate amongst themselves.
- System complexity: It is difficult to design, develop, maintain, and enable an extensive network of IoT devices.
- High probability of system malfunction: Even a small bug can corrupt the entire gamut of associated IoT devices.
What are the benefits of industrial IoT?
Referred to as Industry 4.0 or the 4th wave of the industrial revolution, Industrial IoT (IIoT) is the application of IoT technology in industrial scenarios, especially for control of devices that utilise cloud technology. The two characteristic features of the IoT are automation and connectivity. Therefore, IoT involves the use of several technologies for data transfer, analysis, and communication between devices. These features lead to many interconnected benefits. Below are a few:
- Productivity improvement: Automation of routine tasks helps personnel focus on tasks that need personal skills. It helps minimize the number of employees, ultimately leading to cost reduction for business operations.
- Effective operations management: IoT enables automated control by using multiple smart devices in different areas of operation, such as inventory, supply chain, material tracking, and others.
- Better asset and resource utilisation: Use of interconnected sensors for automatic scheduling and monitoring increases the efficiency of resource utilisation.
- Cost efficiency: The cost decreases due to a decrease in down time, improved production capacity, and efficient management both within the department and across the enterprise.
What are the IoT applications?
Prebuilt software-as-a-service (SaaS) applications that analyse as well as present captured IoT data to businesses. These applications leverage ML algorithms for the analysis of data present in the cloud. This also helps in the detection of glitches, auto-activates alerts for users, and triggers off automatic fixes.
Let us look at a few common uses of IoT applications:
- Creation of new efficiencies in manufacturing through product-quality monitoring and machine monitoring.
- Ring-fencing of high-value assets helps businesses ensure risk mitigation.
- Remote monitoring of patients by medical practitioners using wearable health monitoring devices.
IoT standards and frameworks
IoT standards
The emerging IoT standards will help regulate the industry and create stability while negotiating with firewalls, backend tasks and other things. It will help in laying down a standard for interoperability, portability, and manageability that users otherwise struggle for.
Below are a few standards:
- IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks (6LoWPAN): An open standard defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) that enables a low-power radio to communicate to the Internet, such as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), Z-Wave (for home automation) and 804.15.4.
- Data Distribution Service (DDS): An IoT standard for scalable, high-performance, real-time machine-to-machine (M2M) communications developed by Object Management Group (OMG).
- LiteOS: A Unix-like operating system (OS) which acts as a smart device development platform for wireless sensor networks. It supports wearables, smart homes, intelligent manufacturing applications, smartphones, as well as the Internet of vehicles (IoV).
- Long Range Wide Area Network (LoRaWAN): A protocol for WANs which supports vast networks like smart cities where millions of low-power smart devices are present.
IoT framework
The IoT framework is an ecosystem consisting of many connected devices that communicate continuously with each other over the Internet. These devices transfer and sense data with minimal human intervention. The framework enables smooth communication between connected devices. Therefore, it is called the IoT framework, i.e., the framework that accelerates interaction between ‘things’.
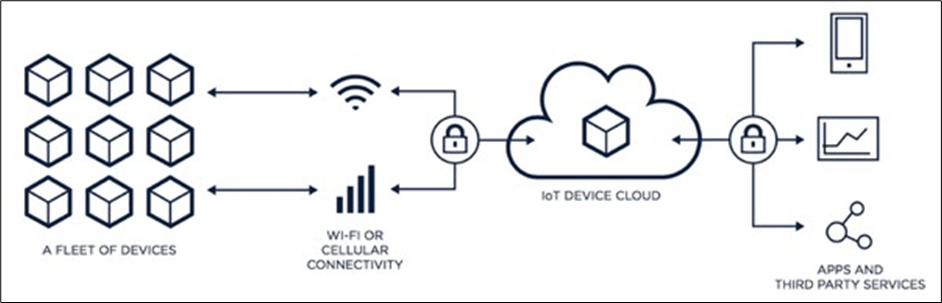
IoT Framework
FAQs
1. What is the future of IoT?
As per industry reports, ~10 billion active IoT devices were used in 2021. The number is expected to go beyond 25 billion by 2030. IoT has limitless potential in the future. It is on its way to creating a more connected world. This wave of connectivity goes beyond smartphones and laptops to connect wearables, homes, cars, and even cities. IoT also promises to protect our planet Earth and make our lives more sustainable. Smart technology helps monitor and control the use of water, natural resources, and energy. It will also help with waste reduction and monitor water and air pollution.
2. What are the five IoT devices?
A device with an attached sensor that transmits data between objects or to people using the Internet is called an IoT device. A few popular IoT devices are:
a. Home Security: A range of sensors, alarms, cameras, and lights controlled using a smartphone are connected through IoT to provide 24×7 security at homes.
b. Activity Trackers: Sensor devices that enable real-time monitoring and transmission of key health indicators. These devices help people track as well as manage physical movements, oxygen levels, appetite, and blood pressure.
c. Augmented Reality Glasses: Wearable computer-enabled glasses that help procure extra information like 3D videos and animations of real-world scenarios for users. Information is available in the lenses of glasses to help users access Internet applications.
d. Google Home Voice Controller: A device that offers voice-enabled services such as thermostats, lights, alarms, and volume control.
e. Amazon Echo Plus Voice Controller: A reliable IoT device that offers voice-enabled services such as setting alarms and timers, answering phone calls, and checking the weather.