We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- How to Handle the Connectivity Conundrum?
- How to Swiftly Switch from WiFi to Cellular?
- dSmartMobility Solution.
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
Contents
The Buzzkill at the Party
Scene: That long-awaited house party. Your friends are over. The music is on. You ask your music player to speak to your Bluetooth device to switch to the 80s Pop station.
Thanks to FTTH, all the appliances in your home speak to each other and work together without a hitch.
That’s when you remember you are out of snacks and have to make a trip to the store.
You walk out and immediately lose connectivity. Oh, dang! Now you’ll have to manually switch back to cellular network. You think to yourself, only if I can bring the magic of FTTH wherever I go. Only if.
How to Handle the Connectivity Conundrum?
FTTH and IoT is all set to make our homes smarter – imagine all our devices and appliances talking to each other and creating an ecosystem of safety and comfort in our homes. But it still begs the question – what about getting the same level of seamless connectivity when you are out and about? We are still manually switching back and forth between WiFi and cellular networks. Then back again to WiFi. The reality is, this is not convenient, yet we continue to endure.
More Devices, More Problems
With a huge number of devices being connected to cellular networks, the result in choke in bandwidth. But the truth is, large chunks of bandwidth of WiFi networks remain unused. There are also several logistical problems to boot and questions to ponder, for example, what about the ROI on WiFi infrastructure? Currently, to use the available WiFi bandwidth, telcos use a connection manager that drains mobile battery and also requires manual intervention to switch on and scan for networks.
How to Swiftly Switch from WiFi to Cellular?
Sensing telcos’ need to tap into the potential of WiFi, STL created a solution tailor-made to make the transition between WiFi and cellular smooth, seamless and automatic. dSmartMobility helps customers automatically switch from LTE to WiFi based on signal strength, throughput, jitter and packet-loss without any manual intervention.
Faster Speeds, Higher Customer Satisfaction
STL’s solution takes all the headaches away from network management while priming it for seamless offload to WiFi. It improves improve network selection, adds policy control capabilities, enables smart decision-making based on analytics. The result, your customers enjoy faster speeds and enhanced voice quality thanks to trusted WiFi hotspots compared to traditional LTE networks.
Say aye to Offload
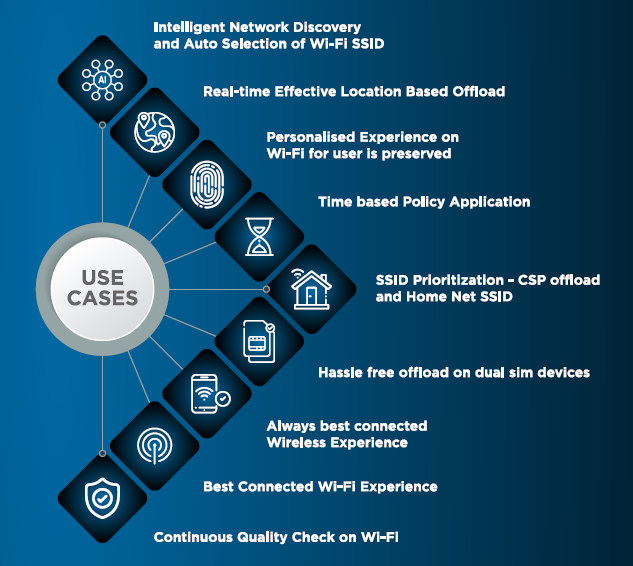
Apart from enabling CSPs to use existing unused WiFi bandwidth, dSmartMobility also provides a platform for Paid Advertising and Partnership Opportunities. The faster speeds will no doubt increase the number of recharges, ultimately creating more revenue. dSmartMobility will also enable CSPs to explore multiple use cases based on Real Time Effective Location-based Offload, Time-based Policy Application, Always Best Connected Wireless Experience etc.
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
An optical fibre cable is a cable type that has a few to hundreds of optical fibres bundled together within a protective plastic coating. They help carry digital data in the form of light pulses across large distances at faster speeds. For this, they need to be installed or deployed either underground or aerially. Standalone fibres cannot be buried or hanged so fibres are bunched together as cables for the transmission of data. This is done to protect the fibre from stress, moisture, temperature changes and other externalities. There are three main components of a optical fibre cable, core (It carries the light and is made of pure silicon dioxide (SiO2) with dopants such as germania, phosphorous pentoxide, or alumina to raise the refractive index; Typical glass cores range from as small as 3.7um up to 200um), Cladding (Cladding surrounds the core and has a lower refractive index than the core, it is also made from the same material as the core; 1% refractive index difference is maintained between the core and cladding; Two commonly used diameters are 125µm and 140µm) and Coating (Protective layer that absorbs shocks, physical damage and moisture; The outside diameter of the coating is typically either 250µm or 500µm; Commonly used material for coatings are acrylate,Silicone, carbon, and polyimide).
An optical fibre cable is made up of the following components: Optical fibres – ranging from one to many. Buffer tubes (with different settings), for protection and cushioning of the fibre. Water protection in the tubes – wet or dry. A central strength member (CSM) is the backbone of all cables. Armoured tapes for stranding to bunch the buffer tubes and strength members together. Sheathing or final covering to provide further protection.
The five main reasons that make this technology innovation disruptive are fast communication speed, infinite bandwidth & capacity, low interference, high tensile strength and secure communication. The major usescases of optical fibre cables include intenet connectivity, computer networking, surgery & dentistry, automotive industry, telephony, lighting & decorations, mechanical inspections, cable television, military applications and space.













