We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- What’s so Unique About Platforms?
- Platforms in a Nutshell
- How has the Emergence of Digital EcosystemsPlayed a Role?
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is WiFi?
- What is 5G NR?
Contents
What’s so Unique About Having Platforms in a Business Model?
You come across the term quite often and might have heard at least once in the last 30 min. It is used and interpreted liberally. So what’s unique about Platforms? Platform has two connotations: as a business model and as a technology infrastructure.
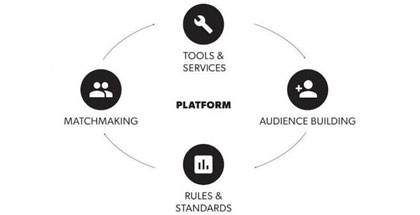
In the book “Invisible Engines”, a digital platform is defined as a foundation of self-service APIs, tools, services, knowledge and support which are arranged as a compelling internal product. It is an assemblage of software frameworks, delivery infrastructure, APIs and architectural remediation, self-service data, customer experience infrastructure powered by advanced analytics engines. Simply put, it is an operating environment with a group of technologies that are used as a foundation upon which other applications, processes or technologies are developed. A platform creates a stable centre of gravity for your tech stack.
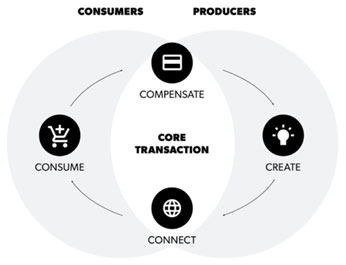
From a business perspective, it is a holistic multi-sided business model that creates value by bringing together consumers and producers; not just a piece of technology stack. To put it in plain speak, just like shopping malls with multiplexes or a city with a prime tourist attraction, a platform is an environment where a strong core anchors and mediates the relationship between a wide range of symbiotics and end-users. You can visualize a platform as a hub, with spokes connecting other products to its centre. The hub binds those disparate products together and orchestrates them in a common mission.
Bill Gates quotes “A platform is when the economic value of everybody that uses it exceeds the value of the company that creates it”. It is only possible due to the large, scalable networks of users and resources that can be accessed on demand. Platforms create communities and markets with network effects that allow users to interact and transact. Platforms don’t own the means of production – instead, they create the means of connection. All platforms obey the following three axioms:
- Network Effects (Metcalfe’s Law and Reed’s Law)
- Near-zero marginal cost of production and distribution
- Expenses (for scaling) level off logarithmically
By that definition, all marketplaces and market networks are platforms built on platforms!! The converse of it need not be true. Platforms are the fundamental markers of 21st-century market society and have inverted all the dynamics of business we have known till date. Below is a table that summarizes its uniqueness
| Platform in a Nutshell | |
| Why do platform firms scale so fast | Sifting production outside, they can have zero marginal costs. Uber, Airbnb and Facebook do not own cars, rooms and content respectively. Not incurring the costs of production, they can scale as fast as they can add partners. |
| Why platforms beat products | Network effects imply that platform value appreciates through use whereas product value depreciates through use. An increasing value proposition, based on positive feedback, overtakes any static or declining value proposition. |
| Why do platforms have high market capitalization but so few employees | They harness users as producers, representing an external labour force, not counted among the traditional workforce. |
| Why the shift in executive mindset is so hard | Executives familiar with managing vertical integration must transition to managing open orchestration, from resources they control to resource their partners must volunteer |
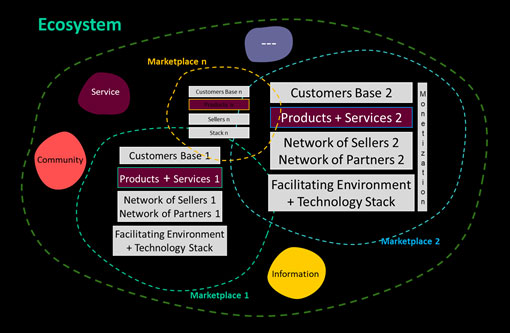
How has the Emergence of Digital EcosystemsPlayed a Role?
Emergence of digital Ecosystems is a triumph of collaborative economy and a real celebration of “The Age of You”. Rather than relying either on the buyer or to buy a bundle from a single source, where a firm acts as a system integrator, Ecosystems allow final customers to have some choice but pick from an expandable menu, which is in turn curated and managed by an ecosystem orchestrator. Therefore Ecosystems become new ways of organizing complementary goods and services that involve a network of interacting producers, suppliers, innovators, customers and regulators collaborating and competing to offer a collective outcome of a complex good or services
Digital ecosystems consist of interacting organizations that are digitally connected and enabled by modularity, and are not managed by hierarchical authority (as in supply chain). In ecosystems, organizations come together by co‑specializing with each other, creating bonds that engender collaboration, without excluding competition with customers at its center. On the B2B side, ecosystems integrate disparate cross-sector or cross-industry platforms, products and services to deliver solutions that matter to the business. In the context of this blog, an ecosystem can be framed as a superset of platforms that successfully serves the needs of a broad number of adjacent verticals.
It is vital to understand this is a metaphor and is a borrowed term from the ecology. The fundamental principles such as interdependence, network patterns, partnerships, feedback loops, and self-organizing their way to sustainability via diversity and innovation hold good for the digital ecosystems.
Sources
- Fritjof Capra on Ecosystems: https://www.ecoliteracy.org/article/ecology-and-community
- Non-traditional B2B Platform: https://www.kloecknermetals.com/
- Platforms and Ecosystems: Enabling the Digital Economy (WEF)
- The Next Great Unbundling: https://a16z.com/2019/09/11/platforms-verticals-unbundling/
- Book: Invisible Engines: https://mitpress.mit.edu/books/invisible-engines
- Roadmap: B2B Marketplaces: Bessemer Venture Partners
- What do you mean by Platform: TM Forum Analysis
- Platform Business Model: https://www.applicoinc.com/blog/what-is-a-platform-business-model/
- What I Talk About When I Talk About Platforms: Martin Fowler
FAQs
What is WiFi?
Put simply, WiFi is a technology that uses radio waves to create a wireless network through which devices like mobile phones, computers, printers, etc., connect to the internet. A wireless router is needed to establish a WiFi hotspot that people in its vicinity may use to access internet services. You’re sure to have encountered such a WiFi hotspot in houses, offices, restaurants, etc.
To get a little more technical, WiFi works by enabling a Wireless Local Area Network or WLAN that allows devices connected to it to exchange signals with the internet via a router. The frequencies of these signals are either 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz bandwidths. These frequencies are much higher than those transmitted to or by radios, mobile phones, and televisions since WiFi signals need to carry significantly higher amounts of data. The networking standards are variants of 802.11, of which there are several (802.11a, 802.11b, 801.11g, etc.).
What is 5G NR?
5G typically refers to the fifth generation of wireless technology. NR, commonly known as New Radio, is a standard developed by the 3GPP Group (Release 15 being the first version introduced back in 2018) outlining the technology required to harness the newly-available millimeter-wave frequencies. The two frequency bands in which 5GNR operates are Frequency Range 1, i.e., Sub 6GHz band (410 MHz to 7125 MHz), and Frequency Range 2, i.e., millimeter-wave (24.25 to 52.6 GHz). Over 4G LTE, 5G NR provides better spectrum utilization, faster data rates, hardware efficiency, and improved signal processing.
From a deployment standpoint, we have Non-Standalone Mode(NSA), Dynamic Spectrum Sharing(DSS), and Standalone Mode (SA). The initial deployments of 5G NR are based on NSA standards, meaning the existing 4G LTE network will operate on the control plane, and 5G NR will be introduced to the user plane. This particular standard was introduced by 3GPP, keeping in mind the industry’s push to faster 5G services rollout while utilizing the existing 4G LTE infrastructure currently in place. On the other hand, operators are also implementing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS) to accelerate the deployment cycle, reducing costs and improving spectrum utilization. In this standard, the same spectrum is shared between the 5G NR and 4G LTE, multiplexing overtime per user demands. Lastly, we have the Standalone Mode (SA), which moves towards a complete 5G based network where both signaling and the information transfer are driven by a 5G cell.
In the future, 5G will enable new services, connect new industries and devices, empower new experiences, and much more, providing mission-critical services, enhanced mobile broadband, and various other things.
a) Enhanced mobile broadband (eMBB) Applications: High device connectivity, High mobile data rates, and Mobile AR & VR applications
b) Ultra-reliable, low-latency communications (uRLLC)Applications: Autonomous vehicles, Drones, Data monitoring, Smart mfg.
c) Massive machine-type communications (mMTC)Applications: Healthcare, Industry 4.0, Logistics, Environmental monitoring, Smart farming, Smart grids














1 Comment
Deepak
November 10, 2020Great article! Thanks for sharing