Cellular networks have evolved in the last two decades. They have transformed to accommodate various technological advancements. They grew from 1G to 4G, and the global telecom networks are now gradually heading towards 5G. The networks will have to evolve accordingly to handle this change. They must transcend the traditional closed networks towards open ones. The new technology will use an Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN). This ORAN Technology provides a more open radio access network architecture than that provided today by telcos. It will increase the interoperability between various vendors and create more efficient networks.
Let us first understand how networks work before understanding Open RAN technology. Then, you will also know how they have transformed in these years.
This article will tell you various points related to O-RAN and answer the question, what is Open RAN technology?
Contents
The evolution of networks
Mobile phones send and receive signals via low-energy radio waves. They first communicate with a base station, and from there, they connect to other phones and base stations. These networks are called cellular networks. Below you can see a diagram showing a cellular network.
Cellular networks started with the launch of 1G in Tokyo in 1979. It used analog radios and wireless technology and was the first Radio Access Network (RAN). After that, the US built the first commercial cellular network in 1983. And with the launch of 2G GSM in Finland, the popularity of cellular networks exploded worldwide.
The European Telecommunications Standard Institute GSM technology was the most popular. Next, Qualcomm developed Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA). But this was only available in North America, South America, Japan, and Korea through the predecessors of Sprint and Verizon.
NTT Docomo commercialized 3G in 2001. There were two types of 3G: UMTS and CDMA2000; they made mobile internet access possible. However, the first cellular technology to use IP for all data packets, including voice, was 4G-LTE. It was launched in December 2009 in Oslo, Norway, and Stockholm. 5G technology started in late 2018 and is the most recent RAN technology.
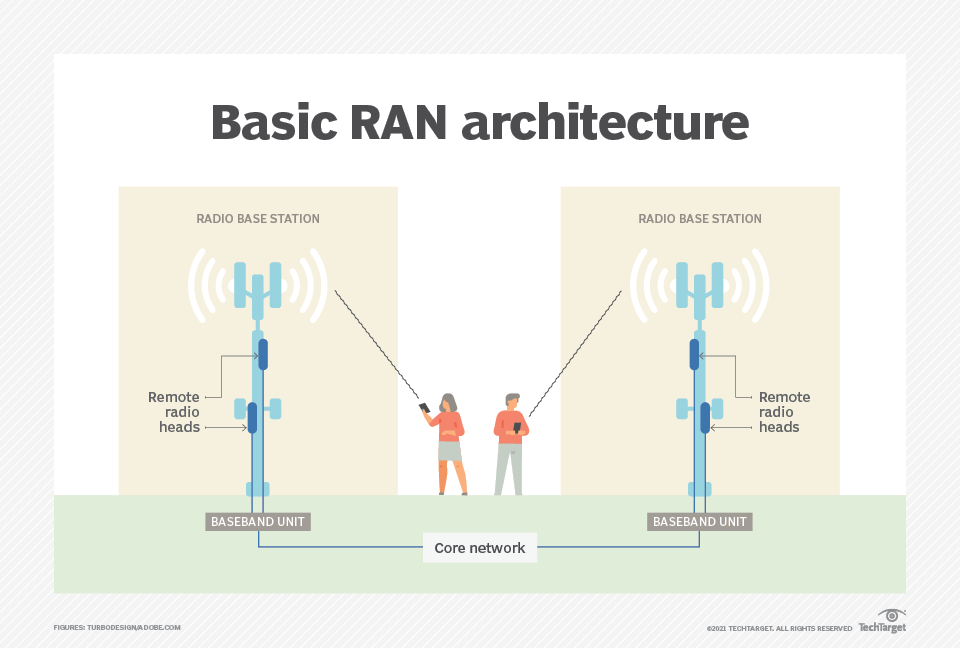
What is the Radio Access Network (RAN)?
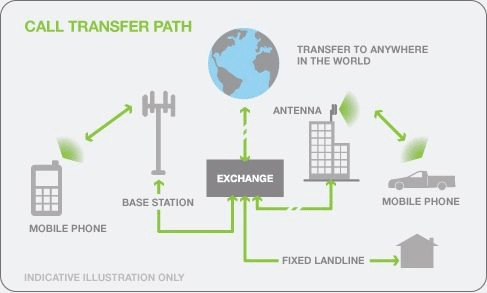
A RAN, or Radio Access Network, helps in managing resources across radio sites. It connects user equipment such as mobiles or computers and the core network with subscriber information, location, etc. The RAN is the radio part of a cellular network of cells containing at least one transceiver.
As mentioned above, they have evolved from the 1st generation to the 5th generation, each generation improving upon the last.
The current RAN technology can transmit voice calls, text messages, video, and audio streaming. It uses the essential components below to communicate this data.
- Antennas: These convert electrical signals to radio waves.
- Radios: These ensure the use of appropriate frequency bands and power levels for communication.
- Baseband Units: This component processes the signals. It contains software and hardware to do that and makes wireless communication possible over radio waves.
What is Open RAN (O-RAN)?
O RAN (Open RAN) refers to industry-wide standards for RAN (Radio Access Network) interfaces; it supports interoperation between vendors’ equipment. As a result, the technology offers network flexibility at a lower cost. Primarily, open RAN enables an interoperability standard for RAN elements. And that includes interoperability for non-proprietary white box hardware and software from different vendors. Therefore, network operators opting for RAN elements with standard interfaces can change their vendors without changing their hardware and software.
The ORAN standards will change the confidential nature of the RAN market, where RAN vendors have proprietary equipment and software.
ORAN separates software and hardware, known as disaggregation. You no longer need to use specific software for particular hardware. Therefore, an O RAN architecture makes the network more flexible and interoperable.
The engineers are developing the ORAN technology using virtual RAN (vRAN) principles and technologies simply because vRAN has improved network malleability and security and reduced CAPEX and OPEX costs.
The O-RAN architecture
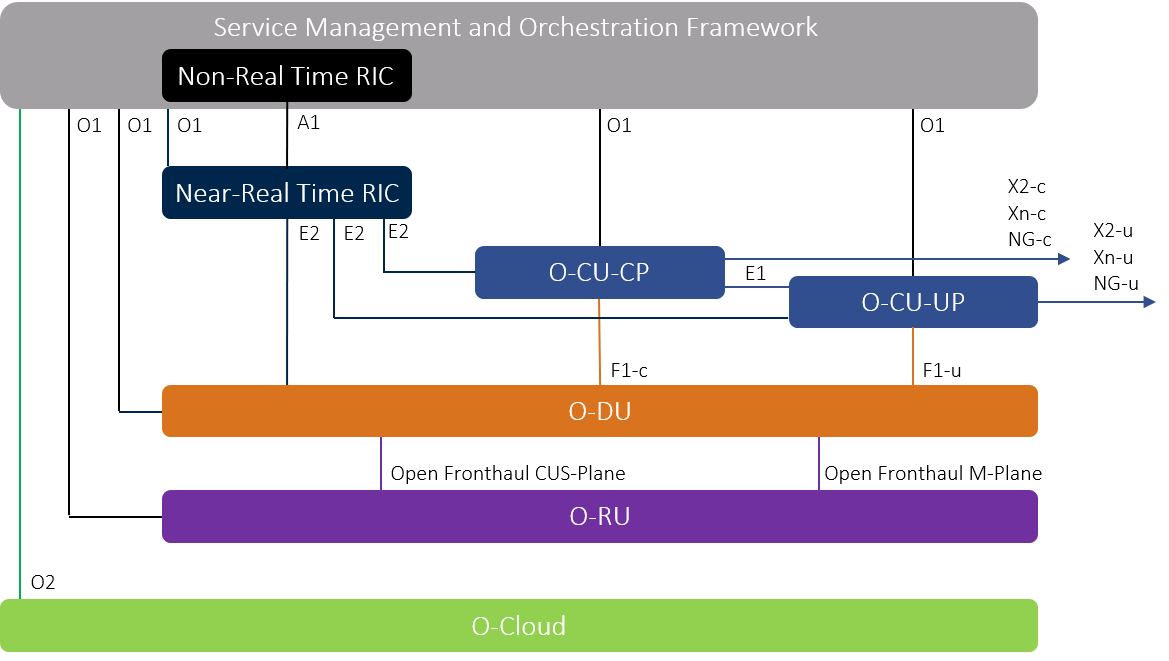
The O-RAN architecture is well documented in the O-RAN alliance. The key elements of the O-RAN architecture are:
- Service Management and Orchestration Framework (SMO)—includes an integration fabric and data services for the functions it manages. It allows managed functions to interoperate and communicate within the O-RAN. The SMO connects to and manages the RICs, O-Cloud, the O-CU, and O-DU.
- RAN Intelligent Controller (RIC) – There are two types of RICs – non-real-time and near-real-time. Both are logical functions for controlling and optimizing the elements and resources of an O-RAN. A near-real-time RIC controls and optimizes elements and resources with granular data collection and communication over the E2 interface. The E2 interface connects the near-real-time RIC with the O-CU and O-DU.
- O-Cloud is a cloud computing platform made up of the physical infrastructure nodes using the O-RAN architecture. It also creates and hosts the various virtual network functions (VNFs) used by the RICs and other infrastructure elements.
- O-RAN central unit (O-CU) – Logical node that hosts a handful of protocols, which are the radio resource control (RRC), service data adaptation protocol (SDAP), and packet data convergence protocol (PDCP).
- O-RAN distributed unit (O-DU) is a logical node that hosts another set of protocols, which are the radio link control (RLC) protocol, medium access control (MAC) protocol, and the physical interface (PHY).
- O-RAN Radio unit (O-RU) – It processes radio frequencies received by the physical layer of the network. The processed radio frequencies are sent to the O-DU through a front haul interface.
How is O-RAN beneficial?
The advantages of O-RAN (Open RAN) are manifold. An open environment means an expanded ecosystem, with more vendors providing the building blocks. In O-RAN, there is more innovation and more options for the operators. They can also add new services.
Some of the other benefits include more market competition and customer choice, lower equipment costs, and improved network performance.
Radio Access Network vendors only offer proprietary equipment and network functions. This is the main reason organizations began developing open RAN standards to break out of that legacy.
Proprietary products are typically more expensive than generic counterparts. Because there aren’t third-party RAN elements that can be integrated into a RAN vendor’s infrastructure, a network operator is stuck with one RAN vendor’s products.
In an open interface, third-party products can communicate with the main RAN vendor’s infrastructure. Network operators can also opt for the less-expensive third-party product that operates on generic hardware. As network operators look to transition to a vRAN architecture for 5G, using open RAN interfaces can reduce the cost of deploying this new technology. When 5G technology advances and changes, network administrators working with open standard-based vRANs can easily send updates to the network infrastructure to accommodate the changes.
Key Components of O-RAN (Open RAN)
The primary components of O-RAN are:
Cloudification: The O-RAN architecture involves hardware and software disaggregation and using RAN applications as cloud-native functions. The 5G RAN has three primary building blocks:
- The Radio Unit
- The Distributed Unit
- The Centralized Unit
Intelligence and automation: ORAN technology uses open management and orchestration with external AI/ML capabilities. Additionally, it has RAN automation interfaces.
Open internal RAN interfaces: 5G ORAN technology includes interfaces defined by 3GPP and the ORAN Alliance. The interfaces are as follows:
- Higher Layers Split
- Inter-node Communication
- O-RAN lower layer split
- Near-Real-Time RIC
O-RAN implementation
ORAN indeed creates new opportunities in radio access network technology. However, operators must consider network security before implementing ORAN technology. It is necessary to have a secure microservices-based architecture for a safe, modern, cloud-native implementation of ORAN.
The O RAN Alliance provides functional compliance to the specifications of components. But for implementation, stakeholders require verification, integration, interoperability, and testing of the commoditized 5G RAN elements. These are necessary to support a plug-n-play model. Therefore, besides commoditization of services, you also need an efficient orchestration of the different ORAN 5G components. Only then can you guarantee stable networks.
The implementation of ORAN technology may increase security risks. First, the API exposure increases because an Open Radio Access Network can have different vendor apps. And each app will expose the APIs. Further, the network will be heterogeneous: apps will be on various network types. So we can’t consider any network to be safe while implementing.
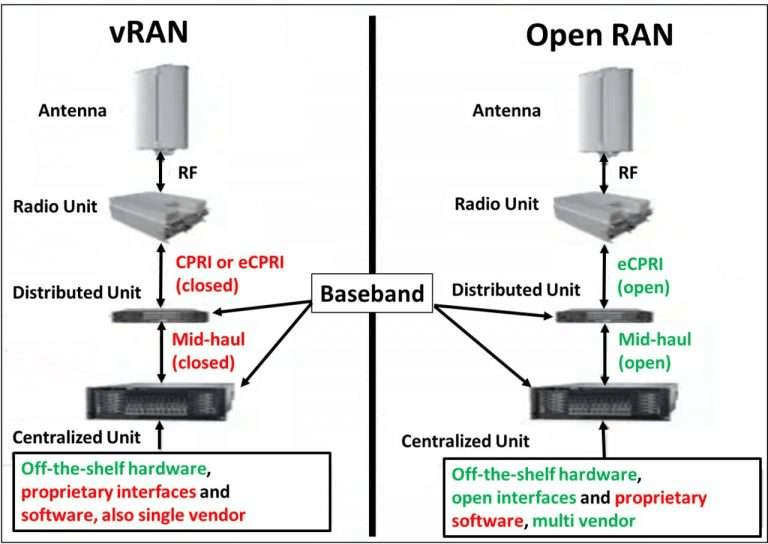
ORAN vs. vRAN
Open RAN is a RAN technology where the software and hardware are open-source. They are according to the open interfaces and standards developed by the community.
vRAN uses a virtualized environment instead of dedicated hardware. A General Purpose Processor runs the baseband functions in vRAN.
So, using vRAN, you can run baseband functions on a commercial off the shelf server. But the interfaces between baseband units and radio units are proprietary. However, ORAN technology also uses open source interfaces.
The reason vendors use vRAN is that it is cost-effective. As you don’t have to build custom hardware, you can develop and run the software on the cloud. That provides a low barrier to entering the RAN market. However, it may not offer great performance as an O RAN technology running on dedicated hardware.
Key terminologies for O-RAN
Over the years, RAN equipment manufacturers have enhanced their products. That compelled the networking industry to go with the ones that provide the best proprietary functionality. However, today, operators want a diverse ecosystem. Therefore, they now have different technological requirements for the network architecture, especially in the 5G RAN.
With any new technology comes new terminologies. These are essential for efficient communication during implementation or troubleshooting. Therefore, open radio access networks also have some key terms.
Below are some of the popular O-RAN terminologies:
O-RAN (with the hyphen) refers to the O-RAN Alliance. It publishes new RAN specifications. In addition, it releases open software for the RAN. It also supports its members in integrating and testing their implementations.
“ORAN” can also mean the Open RAN technology. But O-RAN with the hyphen always means the O-RAN Alliance. You can also see #oRAN or #ORAN hashtags on social networks as a reference to the O-RAN Alliance or the Open RAN movement.
Cloud RAN, a virtualized radio access network or vRAN, runs natively on the cloud. Its architecture is future-proof. Additionally, it includes microservices and containerization.
As mentioned above, Open RAN has three main building blocks:
- Radio Unit (RU)
- Distributed Unit (DU)
- Centralized Unit (CU)
The radio frequency signals are transmitted, received, amplified, and digitized in the RU. The radio unit is near or integrated into the antenna. The DU and CU of the base station are for computation. They send the digitized radio signal into the network. The DU is physically at or near the RU, and the CU is closer to the core.
ORAN 5G means using ORAN technology for 5G communication. Using Open RAN technology, engineers can design energy-efficient base stations for 5G.
FAQs
1. What does RAN stand for?
RANs, or Radio Access Networks, are a significant part of cellular communication. It is responsible for connecting all the individual components of the network. For example, cell phones transmit data through radio waves. And they first connect to a RAN. A Radio Access Network then uses transceivers to connect a cellphone to the core network.
2. What is 5G ORAN?
5G ORAN means using Open RAN technology to communicate using the fifth-generation cellular technology. Disaggregation is necessary for a 5G network; it is one of the ORAN concepts. Therefore, 5G networks will benefit from Open Radio Access Networks. In addition, it will enable interoperability between multiple 5G vendors.
3. What is the RAN Intelligence Controller?
RIC, or RAN intelligence controller, is an O RAN architecture that can run natively on the cloud. It is central to the vRAN network and enables near real-time control, RAN slicing, QoS control, enhanced RRM, etc. Using a RIC, you can create an open ecosystem to develop, deploy, and operate third-party applications. Therefore, improving RAN efficiency and reducing costs.
4.Is V RAN better than O-RAN?
No, vRAN is not better than O RAN technology. It only separates the software and hardware for the baseband. Interfaces between a baseband unit and a radio unit are still proprietary. However, vRAN is cost-efficient as you don’t need dedicated hardware.