We discuss the following topics in this blog:
- New technologies are changing the landscape of CSPs
- How to get the most out of Data?
- Analytics & its Ingredients – AI, Edge Computing and Cloud
- What are the Benefits of Edge Analytics?
- Advanced 5G Use Cases in Telecom
In addition to these topics, we shall also be answering the following FAQs:
- What is an Optical Fibre Cable?
- What is WiFi?
Contents
- 0.1 New technologies are Changing the Landscape of CSPs
- 0.2 How to Get the Most out of Data?
- 0.3 Analytics & its Ingredients – AI, Edge Computing and Cloud
- 0.4 Benefits of Edge Analytics?
- 0.5 Advanced 5G Use Cases in Different Sectors
- 0.6 Energy & Utilities:
- 0.7 Agriculture
- 0.8 Healthcare
- 0.9 Public Safety
- 0.10 Manufacturing
- 0.11 Public Transport
- 0.12 Media & Entertainment
- 0.13 Automotive
- 0.14 Financial Services
- 1 FAQs
New technologies are Changing the Landscape of CSPs
Communication Service Providers (CSPs) are looking to take advantage of data-driven digital transformation and leading towards becoming the Digital Service Providers (DSPs). The rapid change in the Telecom Sector is sheerly defined by the new upcoming technologies like Internet of Things (IoT), Cloud Computing, Edge Computing and Network Function Virtualization (NFV). But the evolution of all these technologies is marked by the revolution called 5G.
5G is the next big thing for CSPs today as it offers them multiple opportunities to move beyond traditional revenue streams and open up new avenues for growth. Typically, 5G in comparison to 4G has the potential to offer speeds of between 1-10 gigs per second which is approximately 20x to 30x faster, 10X reduction in latency and 100X Increased traffic capacity.
With 5G coming into the picture, the single technology that will benefit the most and drive everything will be AI-based Data Analytics. With the evolution of 5G, Data Analytics will be the early adopters as it provides the same benefits which were earlier obstacles for it e.g. – data agility, variety of data, edge computing etc. This will be the foundation for new revenue streams, use cases and even the likelihood for different types of business models within the sector, changing the landscape of CSPs.
How to Get the Most out of Data?
Telcos have always been blessed with the most amount of data with diversified data sources compared to any other industry but unfortunately, they were not able to use it effectively. So, data-rich and insight poor has always been a story of CSPs but this is where AI and ML chips in to drive Intelligent Analytics.
To work on data and get the insights out for decision making, Analytics is a must to have a grip on: –
Analytics & its Ingredients – AI, Edge Computing and Cloud
With 5G and IoT exploding with floods of data, there will be 75 billion connected things and devices by 2025 (Source: Statista) and these devices will be potentially streaming data every second of the day.
But the million-dollar question is, how CSPs can use IoT data to capture, analyze and drive business insights and actions in real-time? There lies the value of streaming analytics, edge, and cloud and how businesses extract actionable insights out of this real-time data.
To capture all the ocean of IoT data, ingesting it, meta-tagging and storing it in the cloud for analysis in the end is not always a smart move. With the speed of 5G and reduced latency, many use cases can take advantage of edge computing and edge analytics to reduce bandwidth cost, time and improve performance e.g., IoT Video Camera Sensor Data, Cloud Gaming, Autonomous Driving etc
Benefits of Edge Analytics?
- Faster, autonomous decision making since insights are identified at the data source, preventing latency
- Lower cost of central data storage and management since less data is stored centrally
- Lower cost of data transmission since less data is communicated to the central data warehouse
- Better security/privacy since the most granular data such as video footage is not stored or communicated
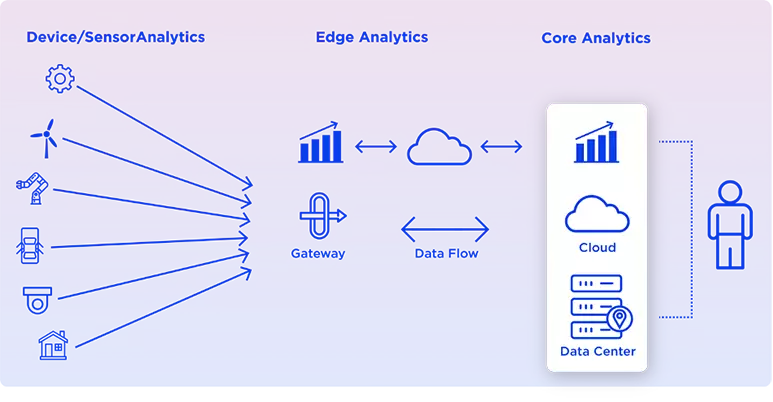
However, for edge analytics to work, we need the support of a data lake & cloud data centre to analyse, test & train machine learning models and store data. After polishing these machine learning models, they can then be pushed back to the edge, making them more adaptive to new and changing circumstances and ultimately intelligent. So practically a hybrid-analytics model is formed to use it as per requirement providing agility to generate insights. Meaning the best of both worlds with some intelligence at the edge for quick action and more at the data lake for predictive and cognitive analytics.
So, hybrid analytics will be appropriate for the following reasons: –
Context: Context allows you to add and integrate to the sensor IoT data with diverse enterprise and legacy data sources for richer context and understanding.
Comparison: Comparative analysis lets you compare the performance of data across different scenarios or timelines to gain deeper insights. For example – How did the performance of one machine compare to a similar one on the same factory floor? How does it compare to one in another location? How did the equipment performance parameters vary over time? etc.
Machine Learning: Huge volumes of data at the cloud/data lake is used (for better sample size) to train and refine models. Once these models are built, they can then be deployed back out to the edge. Meaning models are prepared at the cloud and Personas are derived at the device edge and collectively it is used as an intelligent edge for contextual offers.
Analytics & Reporting: Analytics & Reporting will take the form of interactive data exploration by CSP’s data scientists or data analysts.
Visualization: It is responsible for the creation and visual representation of data.
Key Features of Virtualization: –
- Horizontally and vertically scalable
- Simple Drag & Drop Interface
- Enhanced visualization using R scripting component that brings predictive insights into your business data
- Advanced Visualizations (Leaflets, Mito Plot, SDK Java Scripting)
Real-time Decision Making: The system gathers data in near real-time and takes decisions as per business rules configured by the user and impose the decision to multiple downstream systems such as customer care portal, self-care portal, CRM, PCC, BRM etc. This help CSPs to take decisions in real-time to improve customer experience by: –
- Offering Right Service at Right Time to ensure consumer’s continued association
- Monitoring QoS of High Revenue & Key Account Cell Site
This is exactly where STL’s Intellza marks its success in leading global Tier-1 CSPs by providing a complete packaged solution with a unified data management platform and hybrid analytics model that empowers CSPs in achieving meaningful actionable insights from complex data anywhere, from the edge to AI, in a compliant and secure fashion.
Advanced 5G Use Cases in Different Sectors
5G use cases can be found in a variety of industries, including:
Energy & Utilities:
- The 5G network can provide real-time, flexible electricity flow routing based on generation and consumption levels in various parts of the electrical grid.
- Oil wells outfitted with IoT edge sensors and linked to 5G networks can identify signals in data to predict when wells fall outside of optimal production ranges.
Agriculture
- The 5G network enables a central operator to control this farming machinery remotely.
- Drones can also be used to send live high-quality video streams back to a central control room via the 5G network.
Healthcare
- Telemedicine is a 5G use case that shifts simple consultations to the internet via video calls.
- Apple Watch and Fitbit devices will increasingly be connected to the 5G network, allowing users to diagnose, monitor, and treat chronic diseases.
Public Safety
- Over the 5G network, surveillance cameras can transmit real-time Ultra-High-Definition video streams.
- Thousands of Internet of Things sensors connected to the 5G network can be placed across major infrastructures, such as bridges, to detect vibrations that can be analyzed to determine whether the bridge is functioning properly.
Manufacturing
- 5G data network mobility management, coverage, and quality of service assurance provide the reliable communication required for a wide range of automated guided vehicles such as tractors and pallet movers.
- 5G connectivity and remote monitoring for robotics play an important role in connecting production line robotics.
Public Transport
- 5G enables data transmission in use cases such as high-speed trains and self-driving drones, potentially disrupting these industries.
- Train sensors can detect empty cabins and send data back to the train platform via the 5G network, directing passengers to available cabins.
Media & Entertainment
- Because of 5G’s lower latency and faster network speeds, gaming will shift from the physical console (e.g., PlayStation and Xbox) to the cloud.
- 5G reduces lag times in signals in the AR / VR Augmented Reality / Virtual Reality industries, which could provide a literally dizzying experience for people if the lag time is too long.
Automotive
- Cellular Vehicle-to-Everything (or C-V2X) technology is enabled by 5G, allowing autonomous vehicles to connect to the 5G network and transmit data.
- The 5G network is used by fleet management to monitor multiple data streams from vehicles in real-time, such as GPS positioning, fuel consumption, vehicle faults, and so on.
Financial Services
- Lending money is a huge part of the financial services industry, which 5G use cases can potentially disrupt.
- Another area 5G use cases may disrupt is assets that have financing but generate income, such as vehicles.
FAQs
What is edge analytics?
Edge analytics is a type of analytics that analyses non-central system components such as sensors, switches, and various connected devices. Processing sensor data at edge means insights are gained closer to the devices where the data is collected.
What is edge analytics used for? It allows for faster decision-making, which is especially useful when bandwidth is limited. Given businesses’ increasing reliance on automated, data-driven decision-making, tech behemoths are investing heavily in edge analytics. Edge analytics can help industries like retail, energy, security, manufacturing, and logistics make faster decisions. Enterprises and service providers use Edge devices to transmit, route, process, monitor, filter, translate, and store data passing between networks. Integrated access devices are an example of an edge device.
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks. It enables a new type of network capable of connecting virtually everyone and everything, including machines, objects, and devices.
What is 5G technology intended for? 5G wireless technology is intended to provide more users with higher multi-Gbps peak data speeds, increased reliability, ultra-low latency, increased availability, massive network capacity, and a more uniform user experience. Higher performance and efficiency enable new user experiences and link new industries.
5G will impact every industry, enabling safer transportation, remote healthcare, precision agriculture, and digitized logistics, among other things.
What is 5G Analytics?
3GPP has defined an exclusive Analytics Function called ‘Network Data Analytics Function (NWDAF)’ in the 5G Rel 15 & 16 Specifications. The inclusion of the NWDAF as part of 5G Core simplifies interworking complexities for Analytics solution vendors. 3GPP also defines Standard use cases that can assist any operator in managing subscriber QoE in a complex growing network with Network Automation and the NWDAF as the brain of the Architecture. Content analytics also enables additional revenue generation via anonymized data monetization and targeted marketing.
What are the examples of edge computing?
The following are some edge computing examples:
- Patient Monitoring Devices
Patient data is typically recorded and processed on multiple sensors and monitors that are not linked to a centralized database.
- Applications in the Oil and Gas Industry
Edge computing is the solution for isolated offshore oil rigs when internet access is limited.
- Autonomous Vehicles
This concept is quickly becoming a reality, made possible only by edge computing.
- Manufacturing
Manufacturing companies use edge computing to monitor manufacturing in order to detect production errors and improve product quality.
- Cameras and Security
Only video footage triggering specific triggers is sent to the cloud for remote monitoring and analysis.
- Platforms for Streaming Video Games
Cloud gaming companies install Edge servers to reduce latency and provide a completely responsive and immersive gaming experience as close to the gamers as possible.
Which scenarios do you feel need edge analytics?
The scenarios that are in need of edge data analytics use cases:
- Immediate Updates
Consider the purpose as one of the most obvious ways to determine whether you need to use edge-based analytics. Anything that requires a real-time alert should be kept on-premises, which is where analytics edge is useful.
For instance, track customer behavior and receive instant notifications, intrusion detection alerts, and so on.
- Internet Connectivity
Cloud analytics necessitate internet access. If you don’t have enough bandwidth for whatever reason, you might want to consider edge-based analytics or on-premise server analytics.
- Cybersecurity
Another reason is when your data should not leave your premises. In this case, you can run the analytics solution on edge servers or on-premises servers.
What is the most common use case of edge computing?
The most common edge computing applications are:
- Huge amounts of data, such as driving speed, car condition, surrounding circumstances, and emergency/accident information, must be gathered, processed, and analyzed in real-time to ensure a car autonomously operates safely.
- Traffic management
- Individuals’ medical records and health status are dispersed throughout hospitals, clinics, and other locations or in each patient’s wearables. They can be collected, analyzed, and provided to medical professionals for a complete understanding of each patient’s physical condition.
- The analytics edge computing can assist industrial manufacturing in running normally, efficiently, and effectively in Smart Cities, Smart Homes, and Smart Grids.
- VR (Virtual Reality) and AR (Augmented Reality) have many practical applications, such as training employees to use new equipment, assisting workers in new jobs, and teaching.
Why does 5G need analytics?
Because it already deals with the problem of handling petabytes of data that comes with existing connectivity, the data analytics industry will be the sector where 5G’s full potential will be realized.
The low latency and high speed of 5G will greatly benefit the evolution of analytic scalability. These features enable analysts to collect quickly, clean and analyze large amounts of data.
For example, earlier autonomous car production was limited and a pipedream due to the high latency offered by 2G, 3G, and even 4G networks. However, 5G now provides low latency and better information processing in real-time.
What is cutting-edge analytics?
The explosion of data that organizations must manage is driving demand for solutions to help them extract value and better understand their business and customers. This is where cutting-edge analytics comes in handy.
Analyzing data either at or near a sensor, a network switch, or another connected device after collecting and processing sensor data at the edge means cutting-edge analytics. With the increasing popularity of connected devices as the IoT central evolves, many industries such as retail, manufacturing, transportation, and energy are generating massive amounts of data at the network’s edge. It is real-time data analytics in-situ or on-site where data collection is taking place.