Private 5G networks have gained traction worldwide as regulators allocate more spectrum to enterprises to establish their own private 5G networks. This is a progressive opportunity for companies that require 5G capabilities to implement their transformative applications. Now innovative digital transformation will drive smart factories and the internet of things.
Contents
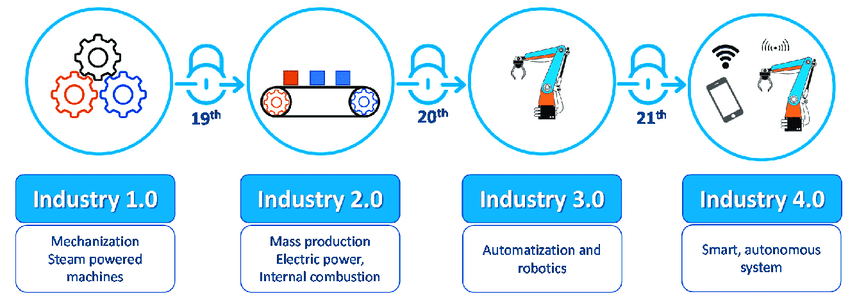
Industry 1.0 to Industry 4.0
Industry 4.0 is synonymous with the fourth industrial revolution and foresees the digital transformation of production, manufacturing, and related industries. It represents a new phase in the industrial value chain organisation, control, and value creation processes.
Industrial and machine manufacturing led to the Industrial revolution. As of now, it has witnessed three stages.
The 18th century saw the advent of steam power and production mechanisation leading to the first industrial revolution.
The Second Industrial Revolution started in the 19th century with the discovery of electricity and assembly line production. It gave way to the Third Industrial Revolution in the late 20th century through partial automation using computers and robots with memory-programmable controls.
We are currently in the Fourth Industrial Revolution phase, characterised by the application of cyber-physical systems and smart machines. It involves extensive modern control systems with embedded software systems, IoT, cloud computing, and cognitive computing.
The role of private 5G networks in industries today
5G private networks can deliver superfast connectivity with high bandwidth and data rates. Moreover, these networks provide scalability and high reliability with ultra-low latency of 1 ms. They can effectively accommodate bulk volumes of IoT-connected sensors and devices. Thus, these networks are apt for businesses that require ultra-low latency to support large networks of connected devices.
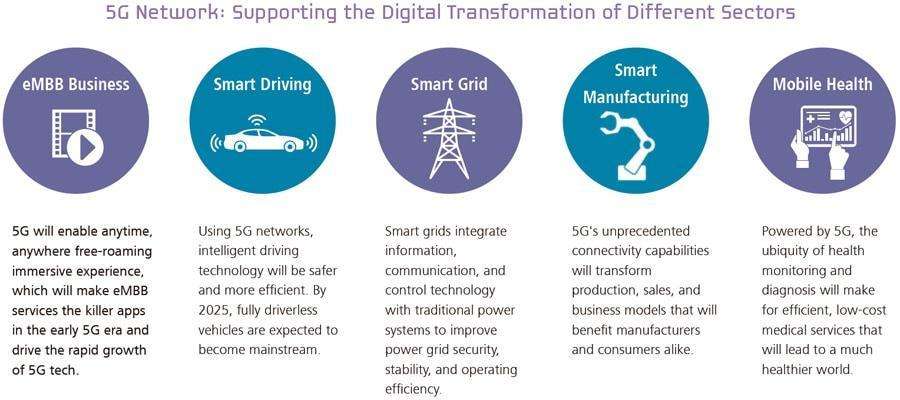
Private 5G networks also provide support for various applications apart from seamless connectivity. They support mission-critical wireless communication with public safety, critical infrastructure, and industrial operations. 5G-enabled technologies lay the foundation of smart factories, smart manufacturing and offer compelling benefits to manufacturers. These networks enable use cases of advanced technologies, such as self-driving machines, collaborative mobile robots, AGVs (automated guided vehicle systems), AR/VR headsets, augmented reality (AR), predictive maintenance, etc.
The impact of industry 4.0 technology on production
5G private network deployments are rising, and analysts forecast strong growth in the forthcoming years.
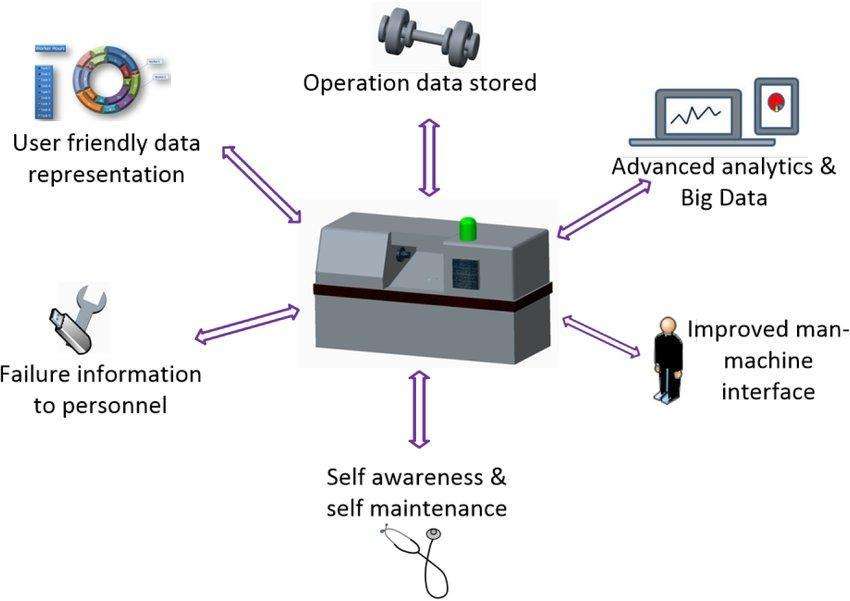
Today, new devices equipped with sensors pave the way for 5G and Industry 4.0 enabling more intelligent and real-time operations. At the same time, cloud providers, machine builders, industrial automation OEMs (original equipment manufacturers), AI technology providers and network vendors collaborate to develop new solutions. These solutions, like predictive maintenance, help industries like manufacturing turn their dream of a 5G future-smart factory into reality.
Also, service providers with 5G licensed spectrum are offering private wireless networks to their enterprise customers as part of a managed services because they see it as a growth opportunity for their business. Automation, analytics and machine-learning algorithms will replace human operators in performing routine tasks. This will lead to quicker, more efficient production with minimal human intervention only needed for system monitoring and maintenance.
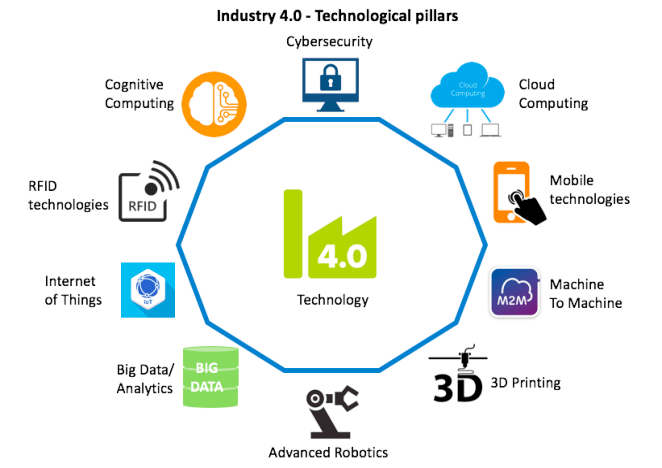
The latest industry-propelling technologies
Internet of Things (IoT)
IoT is the basis of smart factories where sensor-equipped machines can connect with other web-enabled devices. This ensures the collection and analysis of huge amounts of data to aid in informed decision-making.
Cloud computing
The cloud enables the storage and analysis of bulk data more efficiently. It ensures connectivity and integration of the supply chain, engineering, production, sales and distribution, and service.
Edge computing
With Edge computing, data analysis is done where it is created or at the “edge”. This minimises latency time and ensures that data stays near its source, reducing security risks.
Digital twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of factories, production lines, processes, and supply chains. They get data from IoT devices, sensors, and other connected objects to improve workflows and increase productivity.
AI and machine learning (ML)
AI and ML implementation help take full advantage of the massive data generated from various sources. It makes automation of operations and business processes seamless increasing operational efficiency.
Benefits & challenges of industry 4.0
The role of 5G and its ROI opportunities with Industry 4.0 are significant because of the benefits the technology offers. Industry 4.0 technologies improve machine-to-machine communication, automation, decision making, and manufacturing oversight. As a result, they enable us to produce more and faster, allocate resources more efficiently and cost-effectively, and create opportunities for innovation.
They facilitate improved efficiency with less machine downtime and faster batch changeovers. It also promotes automatic track and trace processes and reporting. New Product Introduction (NPIs) also become more efficient. While traditional manufacturing plants operate in silos with minimal collaboration, Industry 4.0 technologies enhance collaborative working and increase knowledge sharing.
Common barriers to digital transformation are:
- Lack of complex Industry 4.0 5G structure management talent or skills
- Cyber security concerns
- Capital expenditure
- Lack of appropriate digital infrastructure
- Lack of knowledge of digitalisation and its application
Way forward for 5G’s impact on industries in the future
As the role of 5G continues to expand, the industrial sector will continue to benefit from the 5G revolution. 5G is expected to be the key to innovation in the future industry landscape with larger capacity, faster speeds, and reduced latency. It has all the potential to create new value across multiple industries and societies.
The contribution of 5G will be significant as it will enable unprecedented levels of connectivity. It can upgrade 4G networks with ultra-reliable low latency communication, superfast broadband, massive machine-type communications, and efficient energy usage. Together, these features will transform various sectors, such as manufacturing, transportation, health and public services.
5G will contribute to industrial advancement in significant ways:
- Use predictive intelligence for faster and more effective inspections
- Improve workplace and worker safety
- Enhance operational effectiveness
Overall, 5G will potentially impact the industry by bridging the digital divide and managing the carbon footprint.
FAQs
What is the need to have private 5G networks?
With the help of private 5G networks, enterprises can have dedicated bandwidth allocated for low-latency use cases. These include robotics and industrial IoT, where enterprises need control over data, networks, and security. Private 5G networks can be tailored for specific business and industry requirements.
The increased reliability and latency make private 5G apt for industrial applications. For example, consider a large manufacturing site, where we may need reliable connectivity both inside and outside. With private 5G, they can connect reliably.
What is private 5G?
Private 5G networks are dedicated non-public mobile networks. They can use licensed/ unlicensed or shared spectrum. Such networks are used to support and enhance the existing capabilities of 4G networks and introduce new possibilities that previous systems could not support. Private 5G network ranges can be low-band, mid-band, or high-band. They can cover anywhere from a few thousand square feet to several square kilometres, depending on the band being used, the power of the radio transmitter, and the user’s needs.
How is 5G used in industry?
5G networks provide telecom operators and manufacturers an opportunity to build smart factories. They support and augment modern technologies such as artificial intelligence, automation, augmented reality, and IoT. With Industry 4.0 and 5G, operators can look forward to creating new revenue streams. Energy, utility, and manufacturing are the significant sectors that have shown immense revenue potential for operators looking for digitisation of industry with 5G technologies.
Why is 5G important to enterprises?
5G technology has the transformational capability for the underlying architecture in core networks. It can effectively promote virtualisation, AI, and automation in enterprises, along with edge computing and network slicing to enable immersive solutions.
Enterprises are in various stages of implementing Industry 4.0 technologies to improve service delivery and develop new solutions. They can achieve reduced cost and increased operational efficiency and can gain a competitive advantage among their peers by meeting rising customer expectations. Enterprises are achieving digital transformation with the help of the cloud, IoT and mobile applications.
What benefits does a 5G network offer businesses?
5G networks with network slicing allow businesses to create virtual networks according to their IT needs. 5G brings network efficiency by drastically bringing down the cost of a mobile network and offering high throughput, low latency, and added security. Businesses can now start using 5G as the primary network like Wi-Fi, unlike 4G, which is used as a backup network. The business can eliminate office wiring by utilising wireless environments in other scenarios.
Businesses can start utilising the capabilities of cloud, mobile and enterprise applications by extending more features and functionality to the frontline employees and their mobile fleet.