Contents
- 1 TCP/IP
vs OSI Model: Differentiating Factors
- 1.1 What is the OSI Model?
- 1.2 History of OSI Model
- 1.3 Characteristics of the OSI Model
- 1.4 Advantages & Disadvantages of the OSI Model
- 1.5 What is the TCP/IP model?
- 1.6 Different layers of TCP/IP are
- 1.7
- 1.7.1 1. Application Layer: This first layer of TCP/IP determines which application will get access to other layers. It has HTTP, FTP, SMTP, Telnet, DNS, SNMP, and RIP.
- 1.7.2 2. Transport Layer: This second layer in TCP/IP layers provides transport between the application layer and session layer with TCP and UDP protocols.
- 1.7.3 3. Internet Layer: This layer helps with host addressing, packaging, and routing functions too. A few core protocols of this TCP/IP model layer are ARP, ICMP, and IGMP. This IGMP is responsible for IPv4 and IPv6 multicasting.
- 1.7.4 4. Network Access Layer: This layer is most important to send and receive TCP/IP packets from a different network. It depends upon the access method, frame format, and medium.
- 1.8 History of TCP/IP
- 1.9 Characteristics of TCP/IP Model
- 1.10 Advantages and disadvantages of TCP/IP
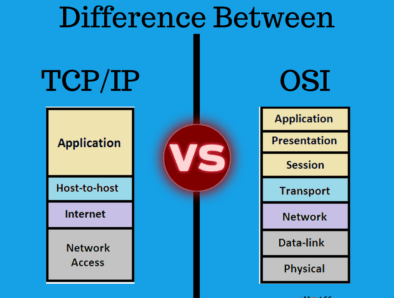
- 1.11 Difference between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model
- 1.12 FAQs
TCP/IP vs OSI Model: Differentiating Factors
If you are thinking about layer 2 switches and layer 3 Ethernet switches, we can guide you about OSI (Open Source Interconnection) model and the network rules based on TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and IP (Internet Protocol). The TCP/ IP model is the older version of the OSI model.
So what’s the difference between them?
We will be explaining the OSI model history, the different layers of the OSI Model, features of the OSI model, the pros and cons of the OSI model, TCP/ IP, features of TCP/ IP, pros, and cons of TCP/ IP, their differences, and a few facts about them.
What is the OSI Model?
OSI model is basically one type of network protocol abstract design. It controls computer packet transfer through different service layers to create a standardized network.
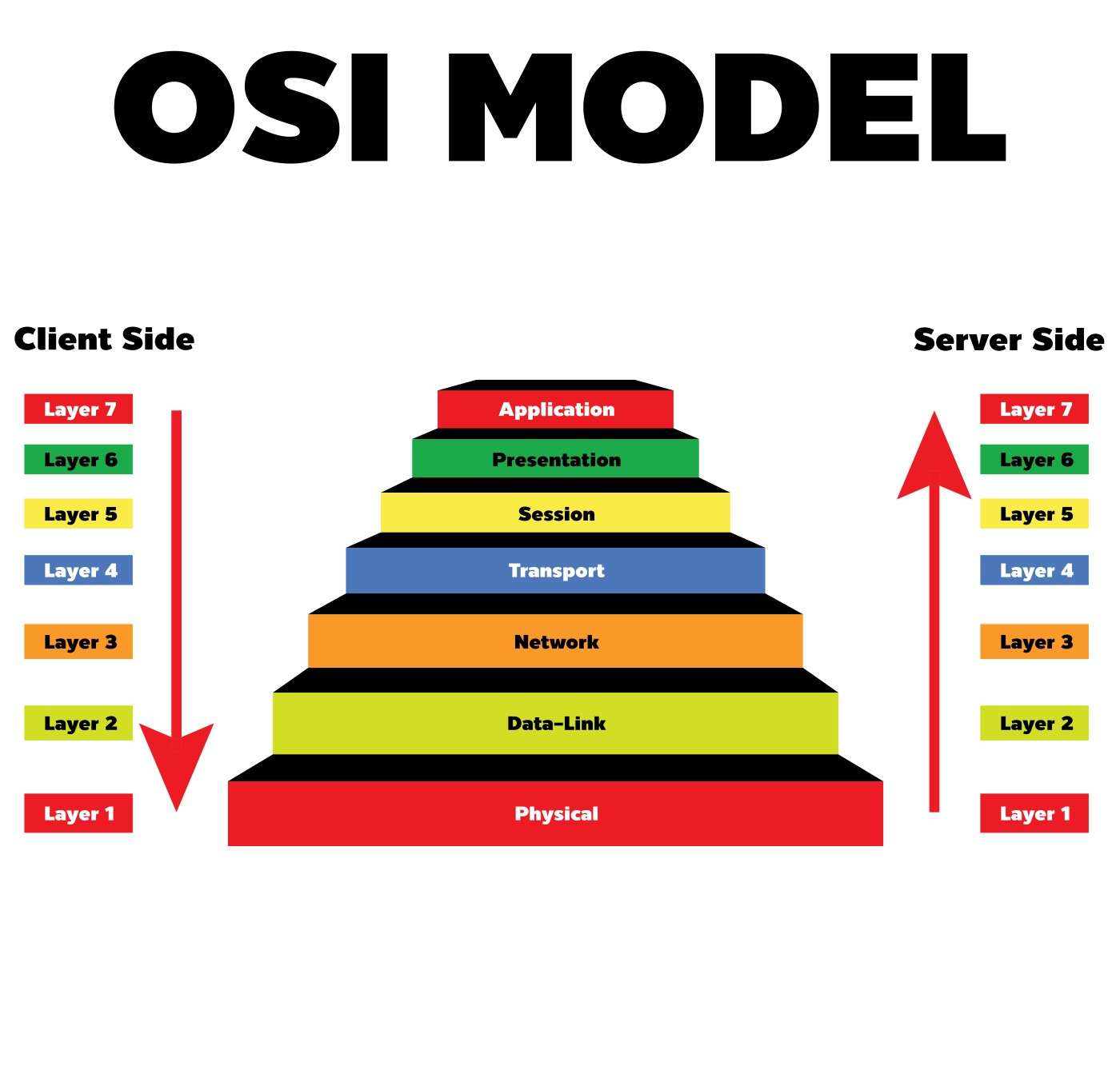
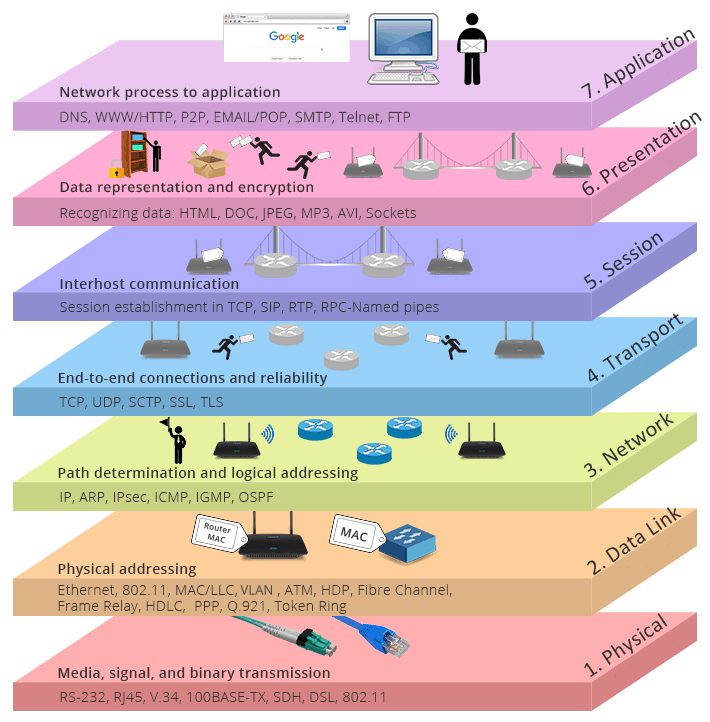
The different layers of the OSI model are
1. Physical Layer: This first physical layer works in between devices, transmission medium, wire-like copper, or optical cable.
2. Data link layer: The second layer maintains the process between network entities and detects errors.
3. Network Layer: This third layer of the OSI model, called the network layer, is important for maintaining connections between different networks.
4. Transport Layer: The fourth layer of the OSI layers maintain transparency of data transfer between different users and send reliable data to the upper layer through flow control.
5. Session Layer: Dialogue connections between computers are maintained by this 5th layer of the OSI model. It also manages the connections between local and remote applications.
6. Presentation Layer: Due to this 6th OSI model layers context between the application layer being established may the upper layer having different syntax and semantics.
7. Application Layer: 7th application layer protocol, used to access by user end to end like web servers and email client servers to get meaningful full data.
History of OSI Model
Here are a few essential landmarks from the records of the OSI model:
- In the past due the 1970s, the ISO performed an application to expand standard requirements and strategies of networking.
- In the yr 1983, the OSI version changed into, to begin with, supposed to be an in-depth specification of real interfaces.
- In 1984, the OSI structure changed into officially followed through ISO as a global standard.
Characteristics of the OSI Model
Here are a few crucial characteristics of the OSI model:
- A layer must best be created in which the particular stages of abstraction are needed in the OSI reference model.
- The characteristic of every layer must be decided on as consistent with the world-over OSI layers’ standardized protocols.
- The wide variety of OSI reference models in computer networks must be huge in order that separate capabilities must now no longer be positioned withinside the identical layer. At the identical time, it must be small sufficient in order that the structure doesn’t emerge as very complicated.
- In the OSI model, every layer is based on the subsequent decreased layer to carry out primitive capabilities. Every stage must capable of offering offerings to the subsequent better layer.
- Changes made in a single layer must now no longer want modifications in different layers.
Advantages & Disadvantages of the OSI Model
Here are the main benefits of using the OSI version:
- It lets you standardize router, switch, motherboard, and different hardware.
- Reduces complexity and standardizes interfaces.
- OSI Facilitates modular engineering.
- Helps you to make certain interoperable technology.
- Helps you to boost up the evolution.
- Protocols may be changed with the aid of using new protocols while technology changes.
- Provide a guide for connection-orientated offerings in addition to connectionless service.
- OSI model layers are a general version of computer networking protocol.
- Supports connectionless and connection-orientated offerings.
- It gives the flexibility to evolve to numerous kinds of protocols.
The following are some disadvantages and disadvantages of using the OSI Model:
- Fitting protocol is a tedious task.
- You can most effectively use the OSI reference model as a reference version.
- It doesn’t outline any particular protocol.
- In the OSI reference model in computer networks, a few offerings are duplicated in lots of layers which include the delivery and statistics hyperlink layers.
- Layers can’t paint in parallel as every layer want to attend to gain statistics from the preceding layer.
What is the TCP/IP model?
Which specific computers will be connected will be selected by the TCP/ IP to create a virtual network for multiple connected computers. This Transmission Control Protocol is a highly reliable designed model layered by TCP/ IP 4 layers models based on fundamental protocols.
Different layers of TCP/IP are
1. Application Layer: This first layer of TCP/IP determines which application will get access to other layers. It has HTTP, FTP, SMTP, Telnet, DNS, SNMP, and RIP.
2. Transport Layer: This second layer in TCP/IP layers provides transport between the application layer and session layer with TCP and UDP protocols.
3. Internet Layer: This layer helps with host addressing, packaging, and routing functions too. A few core protocols of this TCP/IP model layer are ARP, ICMP, and IGMP. This IGMP is responsible for IPv4 and IPv6 multicasting.
4. Network Access Layer: This layer is most important to send and receive TCP/IP packets from a different network. It depends upon the access method, frame format, and medium.
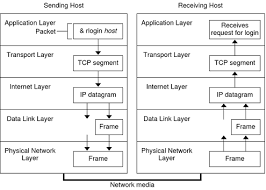
History of TCP/IP
Here are a few vital landmarks from the history of TCP/IP:
- In 1974, Vint Cerf and Bob Kahn posted a paper “A Protocol for Packet Network Interconnection” which describes the TCP/IP Model.
- By 1978, checking out and additional improvements of this language brought about a brand new suite of protocols referred to as TCP/IP.
- In 1982, it became determined that TCP/IP ought to get replaced NCP as the usual language of the ARPAnet.
- On January 1, 1983, ARPAnet converted to TCP/IP,
- ARPAnet completed its existence in 1990. The Internet has given grown from ARPAnet’s roots, and TCP/IP advanced to satisfy the converting necessities of the Internet.
Characteristics of TCP/IP Model
Here are the crucial characteristics of the TCP/IP protocol:
- Stream Data transfer: Applications running on the Application Layer transfer a contiguous movement of bytes to the lowest layers.
- Reliability: The maximum essential function of TCP is dependable records delivery. In order to offer reliability.
- Flow control: Network devices function at special information charges due to different factors like CPU and to be had bandwidth. It can also additionally take place as a sending tool to send information at a miles quicker charge than the receiver can handle.
- Multiplexing: Multitasking is carried out through the use of port numbers.
- Connections: Before utility techniques can send information through the use of TCP, the devices have to set up a connection.
- Full duplex: TCP affords concurrent records streams in each direction.
- Adding greater structures to a network is easy.
- In TCP/IP, the community stays intact till the supply and destination machines had been functioning properly.
- The TCP layer is a connection-orientated protocol.
- TCP gives reliability and guarantees that statistics that arrive out of series have to be positioned back into order.
- TCP/IP layers permit you to put in force go with the drift control, so the sender is in no way a receiver with statistics.
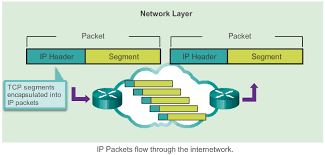
Advantages and disadvantages of TCP/IP
Here are the advantages of using the TCP/IP model:
- It lets you install a connection between different kinds of computers.
- It operates independently of the running system.
- It helps many routing protocols.
- It permits internetworking among organizations.
- The TCP/IP model has a particularly scalable client-server architecture.
- It may be operated independently.
- Supports numerous routing protocols.
- It may be used to set up a connection among computers.
Here are a few disadvantages of using the TCP/IP version:
- TCP/IP is a complex model to install and manage.
- The shallow/overhead of TCP/IP is higher than IPX (Internetwork Packet Exchange).
- In this, model the shipping layer does now no longer assure the delivery of packets.
- Replacing protocol in TCP/IP isn’t always easy.
- It has no clear separation from its services, interfaces, and protocols.
Difference between OSI Model and TCP/IP Model
| OSI Model | TCP IP Model |
| OSI version distinguishes the 3 concepts, namely, services, interfaces, and protocols. | TCP/IP does now no longer have a clean difference among those 3. |
| OSI version offers pointers on how verbal exchange wishes to be done. | TCP/IP protocols format requirements on which the Internet changed evolved. So, TCP/IP is an extra realistic version. |
| In OSI, the version change evolved first after which the protocols in every layer evolved. | In the TCP/IP suite, the protocols had evolved first after which the version changed evolved. |
| The OSI has seven layers. | the TCP/IP has 4 layers. |
| The OSI Model is a logical and conceptual version that defines community verbal exchange utilized by structures open to interconnection and verbal exchange with different structures. | Conversely, TCP/IP lets you decide how a selected laptop ought to be linked to the net and how you could be transmitted among them. |
| OSI header is five bytes. | TCP/IP header length is 20 bytes. |
| OSI refers to Open Systems Interconnection, | TCP/IP refers to Transmission Control Protocol, |
| OSI follows a vertical method. |
TCP/IP
follows a horizontal method.
|
| OSI version, the delivery layer, is the handiest connection-orientated. | The TCP/IP version is each connection-orientated and connectionless. |
| OSI version is evolved via way of means of ISO (International Standard Organization). | TCP Model is evolved via ARPANET (Advanced Research Project Agency Network). |
| OSI version lets you standardize router, switch, motherboard | Different hardware while TCP/IP lets you set up a connection among distinct styles of computers. |
FAQs
- Where is TCP/IP in the OSI Model?
In the OSI model application, session, and presentation layers are connected with the TCP/IP model. This TCP/IP transport layer is connected directly with the OSI transport layer. Even the TCP/ IP internet layer is also connected with the OSI network layer over the internet.
- What is the significance of TCP/IP and OSI to troubleshooting?
In OSI, the version becomes advanced first, after which the protocols in every layer had been advanced. TCP/IP enables the setup of a connection among distinct forms of computers,
while OSI enables standardized routers, switches, motherboards, and different hardware.
- What are some similarities between TCP/IP and OSI?
- Defined Standards: They both have defined standards and frameworks too.
- Same Architecture: Both of them are logical-based models with same to same architectures as they have been built up based on layers.
- Pre-Defined Standards: All predefined standards are not refined again.
- Simple troubleshooting: Troubleshooting is very easy in both models.
- Same transport function and network layers: In the network layer both have the same functions.
4. Is TCP/IP more reliable than OSI?
Yes, TCP/IP is more reliable than the OSI model. Because UDP is available in TCP/ IP model not in the OSI model. It gives transport protection while filing and transferring to other network computers. It makes communication more safeguarded. It can also determine the specific computers which are going to connect to the network. A virtually strong protocol is TCP/IP.