
The Internet of Things (IoT) model has attained more significance in recent times due to the advent of edge analytics. In this data-driven world, the use of data analytics is the key to developing solutions. Edge analytics is automation that helps in data collection and processing.
Contents
Edge analytics and why does it matter?
In many production companies, manufacturing machines, pipelines, and equipment are monitored through IoT. The IoT creates and stores data that might be difficult to manage and process in real-time. With the help of edge analytics, the data is fed in from the IoT devices to process and understand them. Analytics algorithms help humans determine which data is needed and which is not. For example, a faulty running boiler might send data to the IoT device when the temperature exceeds the threshold. Edge analytics processes this data, and an alarm can be raised if there is a problem in the unit. The real advantage of using edge analytics in this scenario is that the latency is reduced. For example, when the threshold is reached, the algorithm can automatically instruct the IoT to shut down the boiler. This can save time and a lot of manual work.
When do businesses prefer to perform analytics at the edge?
Edge analytics can be used for this purpose when there is a need to monitor devices. Businesses can integrate edge analytics with IoT and use them to monitor their production systems. The analytics algorithm processes data in near real-time and provides automated resolution. Even if this is not possible, the data collected from the device can be passed on to the monitoring team. This insightful data will be useful for business to decide what action to take. This method also helps businesses when they scale up. An additional boiler installation can be accompanied by an IoT device, which can automatically start monitoring it.
How does edge analytics work?
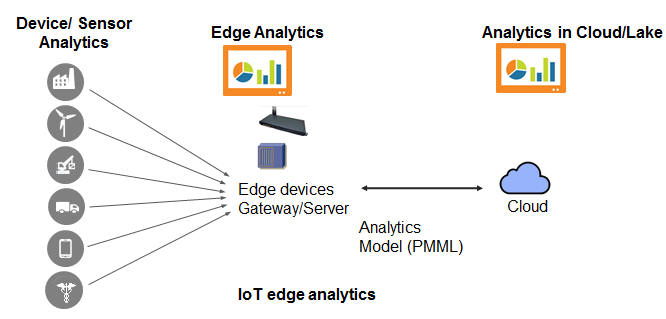
The general workflow of edge analytics integrated tools follows the below pattern:
- Sensors or devices at the edge collect the required data
- Analytics capabilities within IoT devices enable performing analysis at the edge
- If the IoT device needs to take action, it is done based on the analysis results
- Relevant data is transmitted from the edge to the cloud, so businesses can interpret the data by aggregating summarized data from multiple IoT devices
Edge analytics vs. regular analytics
Edge analytics has the same functionality as a regular analytics application, except where the analysis is performed. The main difference is that edge analytics applications need to run on edge devices that may have storage, processing power, or communication limitations. These applications are optimized to work within these limits. In a regular analysis, it takes hours to days or more to put the data together in a report. And because the business is moving so fast, you want to be in front of the game, not behind it. It also means slower cross-platform synchronization. If the analytics software is integrated with other tools, those solutions (and the team members who manage them) will also be affected.
The benefits of edge analytics
- Faster and more autonomous decision-making because the data source identifies insights and there is no waiting time. The main advantage of using edge analytics integration within an IoT device is that there is almost no latency.
- Fewer centralized data stores, reducing the cost of centralized data storage and management.
- Reduces data transfer costs by sending fewer data items to the central data repository. For this reason, the internet bandwidth issues do not pop up at all. The central data repository usually resides in a cloud environment enabled with data replication.
- Improves security and privacy as most crucial data, such as video footage, is not stored or communicated.
Limitations of edge analytics
- The cloud environment is designed for security. Security breaches in the cloud are very costly for business. However, edge security is also important because some edge devices make decisions about the behavior of the actual machine. Violations can result in device disruption, other costly machine failures, or at least incorrect information.
- Some edge analytics systems share output only with the cloud due to bandwidth or storage limitations. In that case, the enterprise does not have the opportunity to see the raw data that led to the analysis shared with the cloud system. Therefore, you need to make sure that your input is processed using the latest analysis software.
Edge analytics use cases
- Analyzing retail customer behavior: Retailers can leverage data from a variety of sensors, including shopping cart tags, parking sensors, and in-store cameras. Retailers can use behavioral targeting to provide a personalized solution for everyone by utilizing analytics on the collected data from the devices.
- Remote monitoring and maintenance in a variety of industries: In industries such as energy and manufacturing, you may need to take immediate action if your machine is not working or needs maintenance. Without the need for centralized data analysis, organizations can more quickly identify signs of failure and take action before system bottlenecks occur.
- Intelligent surveillance: Enterprises can benefit from real-time intrusion detection edge services for security. Edge analytics can detect and track suspicious activity using raw images from surveillance cameras.
Frequently asked questions
1. How is edge analytics different than traditional analytics?
Edge analytics has the same functionality as a regular analytics application, except where the analytics are performed. The main difference is that edge analytics applications need to run on edge devices that may have storage, processing power, or communication limitations. Regular analysis can take hours to days or more to compile the data into a report. This also means slower cross-platform synchronization. These solutions will also be affected if your analytics software is integrated with other tools.
2. What is edge analytics in IoT?
IoT edge analytics is best suited for systems that require rapid data turnover to drive functionality, IoT systems that collect large amounts of data, and IoT devices that function off-network for remote deployment and data security reasons. A typical example of an actual edge analysis is the case of a military drone deployed in a remote location. Drones can technically reach the outside world via satellite communications, but data transfer speeds are too slow to provide real-time feedback effectively. Instead, edge analysis allows for a near-real solution, ensuring a safe mission.
3. What factors drive your business towards edge analytics?
For edge analytics to be useful to your business, your organization needs to know the answers to the following questions:
- Will analyzing data in real-time improve your company’s productivity?
- Need a solution that scales over time?
- Does your company operate in an industry that requires immediate attention when unexpected changes occur?
If the answer to the above questions is yes, then the edge analytics tool is what your business needs for data analysis.
4. What are examples of edge analytics?
Below are a few edge analytics use cases:
- Autonomous vehicles
- Remote monitoring of equipment in manufacturing industries
- Smart grid
- Predictive maintenance
- In-hospital patient monitoring
- Virtualized radio network
- Cloud gaming
- Content delivery
- Traffic management
- Smart home
5. What is edge vs. cloud?
Both cloud and edge analytics are techniques that collect relevant data and use that data to perform data analytics. The main difference between the two is that cloud analytics requires the raw data to be transferred to the cloud for analytics. While cloud analytics has its place, edge analytics has two main advantages. First, edge analytics has much lower latency than cloud analysis. This is because the data is analyzed on-premises. When the data is created, it is often analyzed on the device itself in real-time. The second advantage is that edge analytics does not require a network connection to the cloud. This means that edge analysis can be used in bandwidth-constrained environments or where cloud connectivity is not available.












